Summary
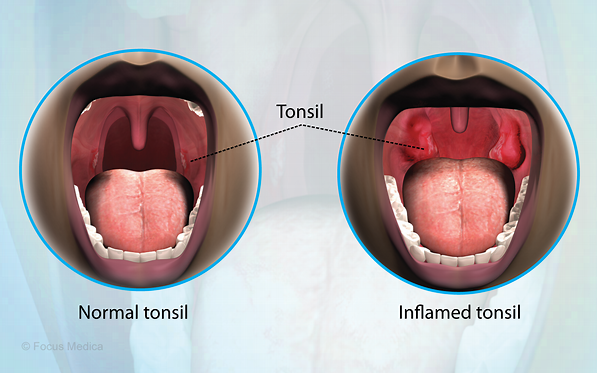
Swelling of tonsils located at the back of the throat due to infection. Tonsils are soft tissue masses which are located on either side of your throat. It is contagious and caused by viruses and bacteria.
Causes:
The common causes are bacterial and viral infection in the tonsils. It is more common in children. The infection is transmitted to another person through coughing or sneezing.
Symptoms:
The symptoms include painful swelling, redness, and white or yellow patches on the tonsils.
Facts
Treatable by a medical professional
Diagnosed by medical professional
Often requires lab test or imaging
Can last several days or weeks
Transmitted through respiratory droplets and indirect contact
Common for ages 5 and younger
Urgent medical attention recommended
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of tonsillitis are inflamed and swollen tonsils. The other causes include:
White or yellow patches on the tonsils
Sore throat
Difficulty or painful swallowing, noted as drooling in young children
Swollen and tender lymph nodes on the sides of the neck
Stiff neck
Fever
A scratchy or muffled voice
Bad breath
Headache
Causes
Tonsillitis is generally caused by a common viral infection such as common cold or sometimes by a bacterial infection.
Tonsillitis spreads through:
Direct contact with infected person
Droplets from sneezing or coughing
Contaminated surfaces, objects, utensils, clothes, etc
Food and water shared with the infected person
Oral sex
The risk factors include:
Age – Children are more prone to infection
Close contact with infected person
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on the physical examination of the throat and other diagnostic tests to identify the cause of infection.
To check for signs of infection of tonsils, nose and ears and for enlargement of spleen.
Gently feeling the swelling in lymph nodes in the neck.
Secretion sample from throat examined microscopically.
To assess the levels of blood cells and determine the cause of tonsillitis.
Treatments
While viral tonsillitis is treated by a few remedial measures, bacterial tonsillitis is treated using antibiotics. Severe and frequent tonsillitis requires surgical removal of the tonsils.
Complications
Complications from bacterial tonsillitis in children, particularly Streptococcus infection:
-
Difficulty in breathing as it blocks the throat
-
Breathing disruption during sleep
-
Spread of infection to deeper tissues, known as tonsillar cellulitis
-
Collection of pus behind the tonsils
-
Rheumatic fever, an inflammatory condition that affects the heart and joints
-
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, inflammation of the kidneys resulting in inadequate waste removal from the body
Prevention
-
Stay away from infected persons
-
Wash your hands thoroughly before cooking or eating
-
Wash your hands every time you use the bathroom
-
Avoid sharing food, water, utensils, water bottles, etc.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
-
Is this a serious infection?
-
Is surgery necessary?
-
Should the patient be isolated during infection?
-
How to prevent spread of infection?
-
Are diet and lifestyle changes necessary to manage the infection?
Nutrition
FOODS TO EATFOODS TO AVOIDFoods to eat:
lukewarm beverages: e.g. ice water, clear juices, chicken broths
Soft foods: e.g. baked apples, baked pears, roasted carrots, mashed potatoes, winter squash, plain pasta, rice
Foods to avoid:
Solid foods e.g. pizza crusts, hard crackers, and crisp cookies
Hot liquids and foods
-